Early biofeedback equipment. Early biofeedback equipment.
| Time
| 1960s and 1970s |
| Title
| Biofeedback emerges in United States and Europe |
| Event
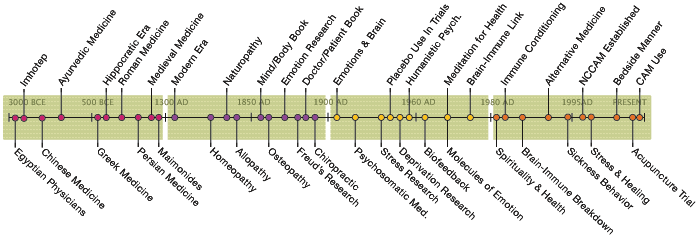
| Researchers focus on new biofeedback techniques, in which patients learn to control unconscious processes. Patients watch monitoring devices that track things like heart rate or blood pressure. By observing how their different actions affect data readouts, patients can start to voluntarily regulate certain body functions. For instance, a person can be trained to lower his own blood pressure. Some controversy exists regarding the efficacy of biofeedback methods. |
|
The mind and body are inextricably linked in biofeedback. (See "body" for more).
|
Mental control alters brain activity, blood pressure, pain perception, heart rate, and other functions that are normally involuntary. Research proves that humans possess more control over so-called involuntary bodily function than once thought possible. When it first emerges, many scientists hope biofeedback will give patients major mental control over their bodies, making drug treatments unnecessary. Some researchers even believe people can “will” greater creativity by changing their brainwave patterns.
Today, most scientists agree that those hopes were not realistic. Still, biofeedback remains a useful tool for creating mindful health.
|
Biofeedback is a secular practice.
|
|