|
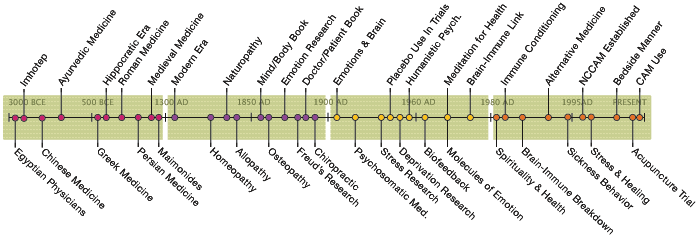
Andreas Vesalius, author of the first real anatomy textbook, upsets the reigning opinion that mind and emotion are centered in the heart. Instead, through illegal dissection, he proves that the brain and nervous system house emotion. French philosopher and mathematician Descartes coins the phrase cogito ergo sum (‘I think, therefore I am’). His philosophy equates the mind with the human soul or consciousness. According to this philosophy, the body can interact with the soul, but it is still merely a physical machine, secondary to and separate from the soul. In 1664 physician Thomas Willis publishes his seminal book of accurate engravings of the human brain based on anatomical dissections: Cerebri Anatome (On the Anatomy of the Brain).
|
The modern era stresses the importance of scientific observation. Copernicus, Galileo, Descartes, Bacon, and others set the standards for gathering scientific data through observation. This leads to a very mechanical interpretation of the body in 17th century Europe. Parts and systems are considered separate, independent and ultimately replaceable. Diagnosis and treatment is also based on data, which is gathered from the outside in.
|
Spirituality and the soul are considered matters of the church. And, at the beginning of this period, virtually all of healthcare in the West is carried out by clergy in hospitals that were built and supported by the church. However, the practice of medicine becomes more a secular discipline towards the end of the 16th century, when physicians begin to be certified by the state. The split between religion and science widens toward the end of this period.
|